
Generally, the value of an asset is measured at market fair value. The market data of different independent sources helps to determine the value. The fair value may fluctuate more often than the market value depending on risk factors. The fair value estimate determines the price an asset will be paid. This is a useful tool for investors to make financial decisions.
Financial instruments are assessed using models that use market data to determine their fair value. These models account for the counterparty risk and liquidity risk of the instruments. An independent audit can validate the models. They might also include market factors. These factors include the interest of the parties, the future goals of the parties and the risk of a market decline. These models can also be based on the type and amount of an instrument. They can contain equity instruments as well as debt instruments. You can also use the models to measure financial instruments using cost, volatility and correlation parameters.
Financial instruments must be valued at fair value. The models must account for all market participants. The market consensus and current bid and asking price are part of the models. An investor can use these factors to calculate the stock's fair value. A stock's price and fair value ratio can also help determine its value relative to it. If the ratio is below one, the stock is considered to be undervalued, while if it is above one, the stock is considered to be overvalued.
The transactional value of equity instruments is measured, while that of derivatives and other debt instruments is measured at market level. The assets to acquired will be subject to the current asking value, while the liabilities to issue will be subject to the current offer price. A stock's market fair value is the price paid for it at the time it is sold or bought.
Fair-value figures can also be published by financial websites prior to the opening of the market. Investors will find this useful as it helps them to assess the value of their investment before it is traded. Many investors may discover that the fair value of stock fluctuates more frequently then the market value. These fluctuations can affect an investor's decision to invest, and could lead to a loss or a profit.
The fair market value of financial instruments is dependent on the interests of each party. The fair value is determined using the hypothetical return that an investor would get on his investment and the interest received by the asset. This value is used for calculating the price you will pay to purchase the stock. While fair value is commonly used to determine the asset's worth and to estimate a business’ growth potential, it also serves to evaluate a company's financial position.
FAQ
What's the difference among marketable and unmarketable securities, exactly?
Non-marketable securities are less liquid, have lower trading volumes and incur higher transaction costs. Marketable securities, on the other hand, are traded on exchanges and therefore have greater liquidity and trading volume. They also offer better price discovery mechanisms as they trade at all times. However, there are some exceptions to the rule. Some mutual funds, for example, are restricted to institutional investors only and cannot trade on the public markets.
Non-marketable securities tend to be riskier than marketable ones. They typically have lower yields than marketable securities and require higher initial capital deposit. Marketable securities are typically safer and easier to handle than nonmarketable ones.
For example, a bond issued in large numbers is more likely to be repaid than a bond issued in small quantities. The reason for this is that the former might have a strong balance, while those issued by smaller businesses may not.
Because of the potential for higher portfolio returns, investors prefer to own marketable securities.
What is a bond?
A bond agreement between two people where money is transferred to purchase goods or services. It is also known as a contract.
A bond is typically written on paper, signed by both parties. This document details the date, amount owed, interest rates, and other pertinent information.
A bond is used to cover risks, such as when a business goes bust or someone makes a mistake.
Bonds can often be combined with other loans such as mortgages. The borrower will have to repay the loan and pay any interest.
Bonds can also raise money to finance large projects like the building of bridges and roads or hospitals.
A bond becomes due upon maturity. This means that the bond owner gets the principal amount plus any interest.
If a bond isn't paid back, the lender will lose its money.
What is the difference?
Brokers are specialists in the sale and purchase of stocks and other securities for individuals and companies. They manage all paperwork.
Financial advisors are specialists in personal finance. They help clients plan for retirement and prepare for emergency situations to reach their financial goals.
Financial advisors can be employed by banks, financial companies, and other institutions. Or they may work independently as fee-only professionals.
Take classes in accounting, marketing, and finance if you're looking to get a job in the financial industry. Additionally, you will need to be familiar with the different types and investment options available.
Statistics
- "If all of your money's in one stock, you could potentially lose 50% of it overnight," Moore says. (nerdwallet.com)
- Even if you find talent for trading stocks, allocating more than 10% of your portfolio to an individual stock can expose your savings to too much volatility. (nerdwallet.com)
- Ratchet down that 10% if you don't yet have a healthy emergency fund and 10% to 15% of your income funneled into a retirement savings account. (nerdwallet.com)
- Individuals with very limited financial experience are either terrified by horror stories of average investors losing 50% of their portfolio value or are beguiled by "hot tips" that bear the promise of huge rewards but seldom pay off. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to create a trading plan
A trading plan helps you manage your money effectively. This allows you to see how much money you have and what your goals might be.
Before creating a trading plan, it is important to consider your goals. You might want to save money, earn income, or spend less. You might want to invest your money in shares and bonds if it's saving you money. If you're earning interest, you could put some into a savings account or buy a house. If you are looking to spend less, you might be tempted to take a vacation or purchase something for yourself.
Once you know what you want to do with your money, you'll need to work out how much you have to start with. This will depend on where you live and if you have any loans or debts. It's also important to think about how much you make every week or month. Your income is the amount you earn after taxes.
Next, you need to make sure that you have enough money to cover your expenses. These include rent, bills, food, travel expenses, and everything else that you might need to pay. These all add up to your monthly expense.
Finally, figure out what amount you have left over at month's end. That's your net disposable income.
You now have all the information you need to make the most of your money.
You can download one from the internet to get started with a basic trading plan. You could also ask someone who is familiar with investing to guide you in building one.
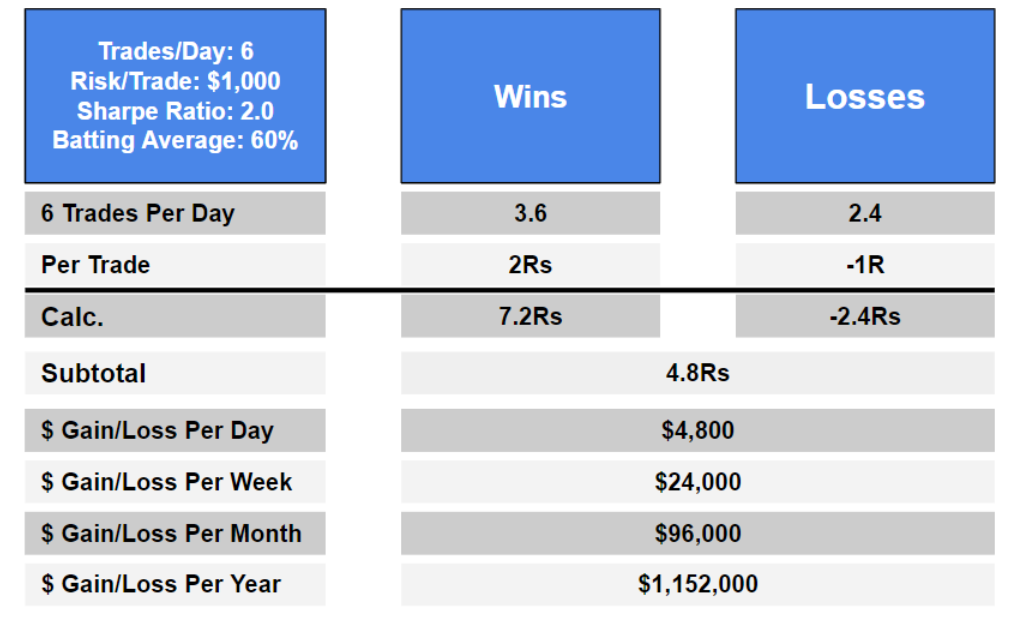
For example, here's a simple spreadsheet you can open in Microsoft Excel.
This will show all of your income and expenses so far. Notice that it includes your current bank balance and investment portfolio.
Here's another example. This was designed by a financial professional.
It will allow you to calculate the risk that you are able to afford.
Don't attempt to predict the past. Instead, put your focus on the present and how you can use it wisely.